 |
 |
|
|
| |
|
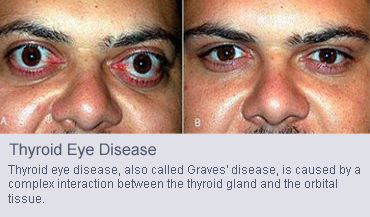
Generally, the symptoms range from eyelid retraction, tearing, ocular irritation, redness, double vision, and pain to loss of vision. Although many patients with thyroid eye disease will have abnormal blood tests for thyroid hormone levels, there are some people who get the eye symptoms even though the hormone levels are normal.
|
|
| If you are newly diagnosed with thyroid eye disease, your eye doctor may ask you to see an endocrinologist or internist to check your hormone levels. The doctor may recommend ablation of the overactive thyroid gland, or taking oral thyroid medication when the gland is underactive. This can be done with anti-inflammatory agents (steroids), radiation and surgery to enlarge the bony orbit. While it is important that hormone levels are kept as close to normal as possible, this will not guarantee that a patient will not develop thyroid eye disease. |
|
| Preoperative Assessment: |
| The most important part of this examination is to determine whether compression of the optic nerve is present causing loss of vision. To determine this visual acuity, color vision, automated visual field testing and examination of the optic nerve head are performed. In addition, biomicroscopic examination including measurement of the pressure inside the eye is performed.
|
| Patients with evidence of visual loss are commonly treated with oral steroids to decrease the amount of inflammation. If the visual loss is significant or the steroids are ineffective, patients are offered orbital decompression. In some severe cases of visual loss or in-patients who fail orbital decompression, we commonly recommend orbital irradiation.
|
| Patients without visual loss but evidence of dryness of the eyes are treated with topical lubricants and plugs in the tear drainage system. If this is ineffective, we often recommend orbital decompression and/or eyelid surgery to improve the corneal wetting due to improved eyelid closure. |
| |
| Operation: |
Prior to surgery, the nursing staff takes care of the lab work and starts an IV. An anesthesiologist will discuss anesthesia prior to surgery. Most patients can expect to stay overnight after surgery. Surgery generally lasts 1 1/2 to 2 hours and each eye operated on will be patched shut.
Patients that undergo eyelid surgery can expect to have a short outpatient stay. Similarly patients are asked to arrive 1-2 hours prior to surgery for appropriate lab work. In general the patients eyes are not patched shut but a dressing is placed on the eyelid only. Surgery lasts approximately 1/12 - 3 hours. |
| |
| Postoperative Attention: |
| After orbital decompression the patient's dressings are removed at 24 hours. The patient may be instructed to clean the wounds with a sterile saline or hydrogen peroxide solution and antibiotic ointment is placed in the eyes and on the wounds twice daily. Patients are generally started on oral antibiotics and pain medication. It is not uncommon for patients to be placed on oral steroids for a short term after surgery. A follow up appointment with your physician will be scheduled within 5-7 days. |